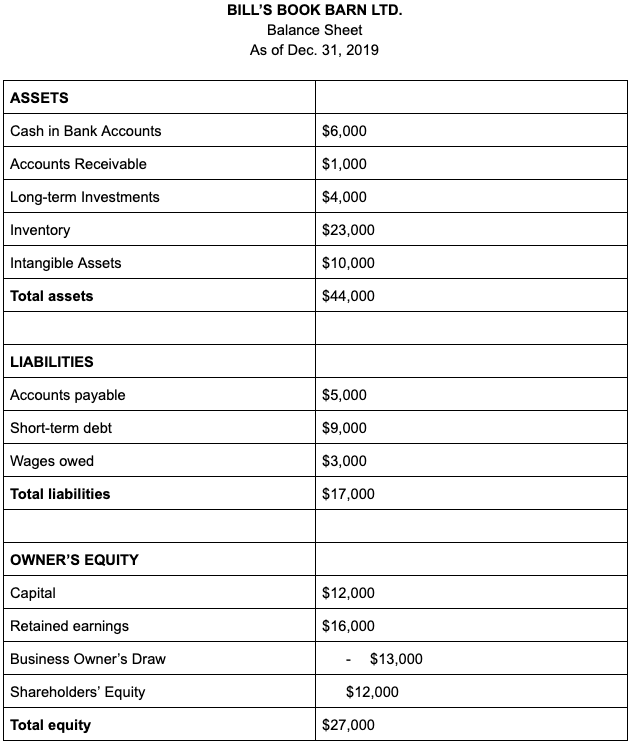
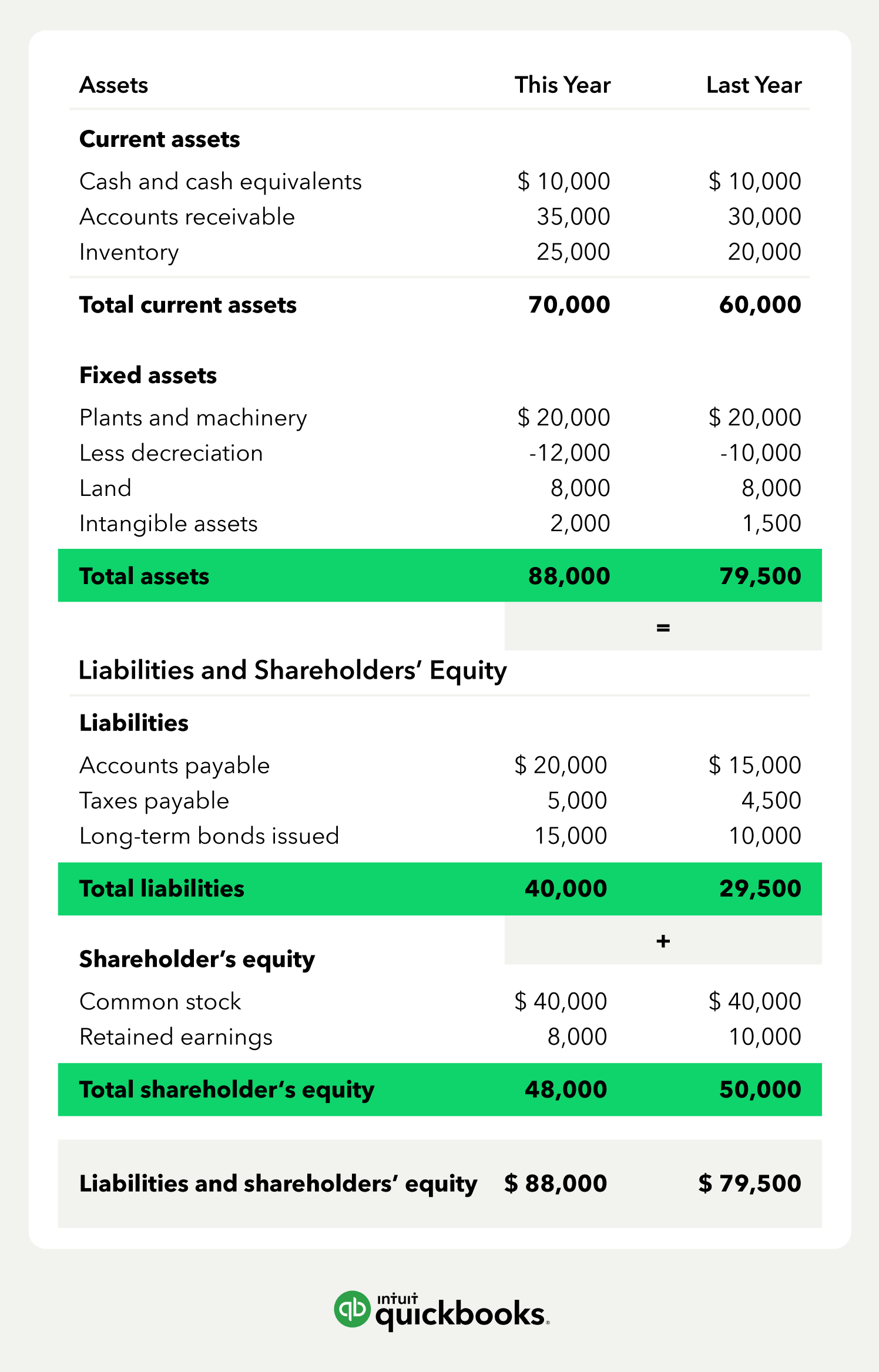
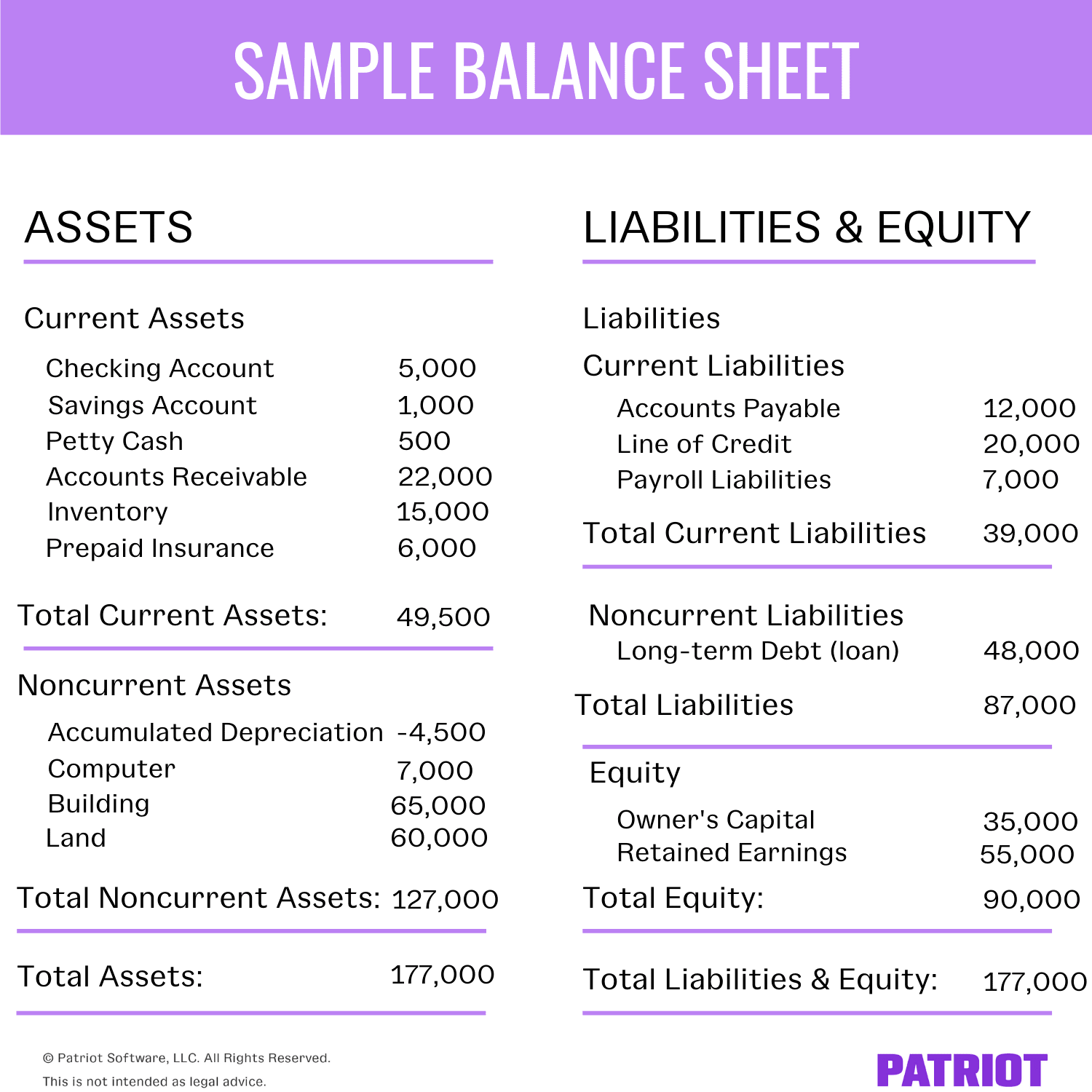
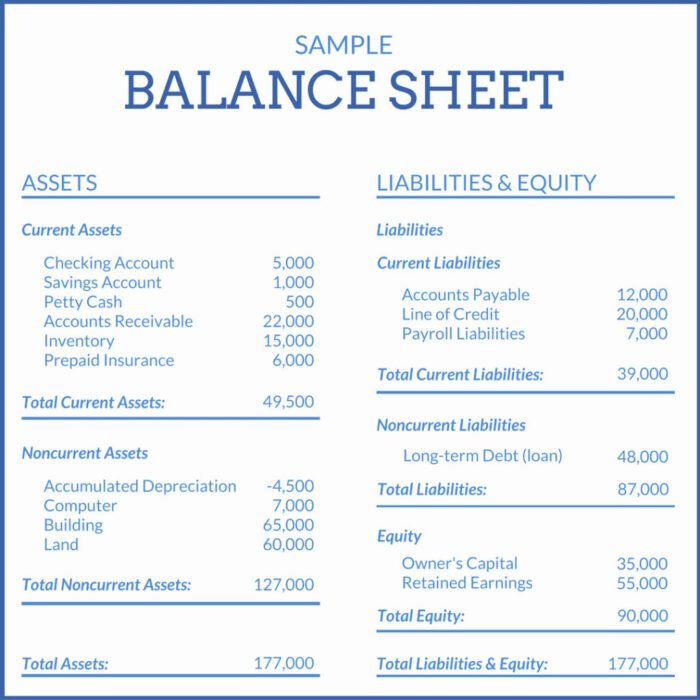
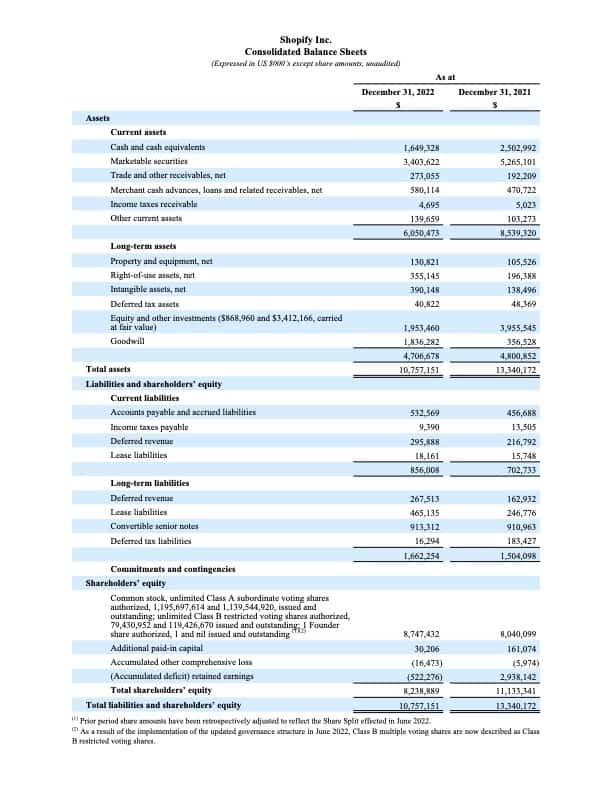
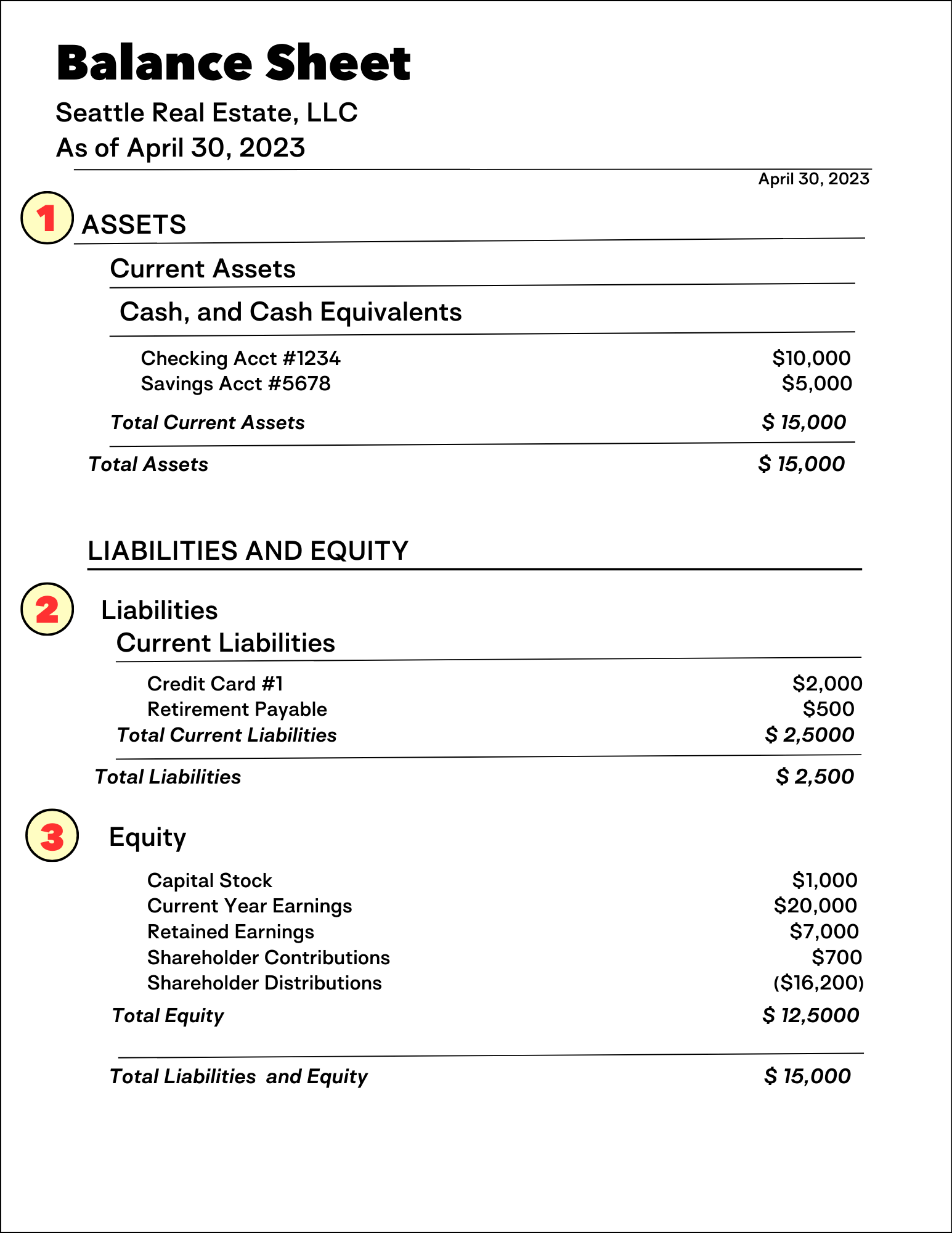
How To Read A Balance Sheet Of A Company - The balance sheet is a key financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company's finances. A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. It’s a snapshot of a company’s financial position, as broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity. The balance sheet is split into three sections: It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is one of the three key financial statements. How to read a balance sheet? Reading a balance sheet is important in determining the financial health of a company. Balance sheets serve two very different. It shows what your business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and how much has been invested by the owners (equity) at a specific point in time.
The balance sheet is split into three sections: A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. It shows what your business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and how much has been invested by the owners (equity) at a specific point in time. Balance sheets serve two very different. It’s a snapshot of a company’s financial position, as broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity. How to read a balance sheet? Reading a balance sheet is important in determining the financial health of a company. The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is one of the three key financial statements. It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. This page explains a balance sheet, why it’s essential, and how to read and create one.
It shows what your business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and how much has been invested by the owners (equity) at a specific point in time. This page explains a balance sheet, why it’s essential, and how to read and create one. The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is one of the three key financial statements. It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. Balance sheets serve two very different. The balance sheet is split into three sections: A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. How to read a balance sheet? The balance sheet is a key financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company's finances. It’s a snapshot of a company’s financial position, as broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity.
How read your balance sheet and actions to take
It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. The balance sheet is split into three sections: A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. The balance sheet is a key financial statement that provides a snapshot of.
How to Read a Balance Sheet Bench Accounting
This page explains a balance sheet, why it’s essential, and how to read and create one. A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. Reading a balance sheet is.
How to Read & Prepare a Balance Sheet QuickBooks
Balance sheets serve two very different. It’s a snapshot of a company’s financial position, as broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity. Reading a balance sheet is important in determining the financial health of a company. It shows what your business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and how much has been invested by the owners (equity) at a specific.
How to Read & Understand a Balance Sheet HBS Online
It’s a snapshot of a company’s financial position, as broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity. A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. It shows what your business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and how much has been invested by the owners (equity) at a specific point in time. This page.
How To Read And Understand A Balance Sheet Business Explained Lights
It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is one of the three key financial statements. A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. This page.
How to read and understand financial statements
It’s a snapshot of a company’s financial position, as broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity. It shows what your business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and how much has been invested by the owners (equity) at a specific point in time. Balance sheets serve two very different. It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to.
How to Read a Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a key financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company's finances. This page explains a balance sheet, why it’s essential, and how to read and create one. The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is one of the three key financial statements. How to read a balance sheet? It’s a snapshot.
How to Read a Balance Sheet The Motley Fool Canada
The balance sheet is a key financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company's finances. It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. Balance sheets serve two very.
How to Read a Balance Sheet?
The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is one of the three key financial statements. Reading a balance sheet is important in determining the financial health of a company. This page explains a balance sheet, why it’s essential, and how to read and create one. The balance sheet is a key financial statement that provides a.
How to read Financial Statements of a Company? Trade Brains
A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. It’s a snapshot of a company’s financial position, as broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity. It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. Balance sheets serve two very.
It Shows What Your Business Owns (Assets), What It Owes (Liabilities), And How Much Has Been Invested By The Owners (Equity) At A Specific Point In Time.
A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. This page explains a balance sheet, why it’s essential, and how to read and create one. The balance sheet is a key financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company's finances. The balance sheet is split into three sections:
How To Read A Balance Sheet?
It's important to know how to read a balance sheet to understand what a company owns and owes at a single point in time. Reading a balance sheet is important in determining the financial health of a company. The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is one of the three key financial statements. Balance sheets serve two very different.