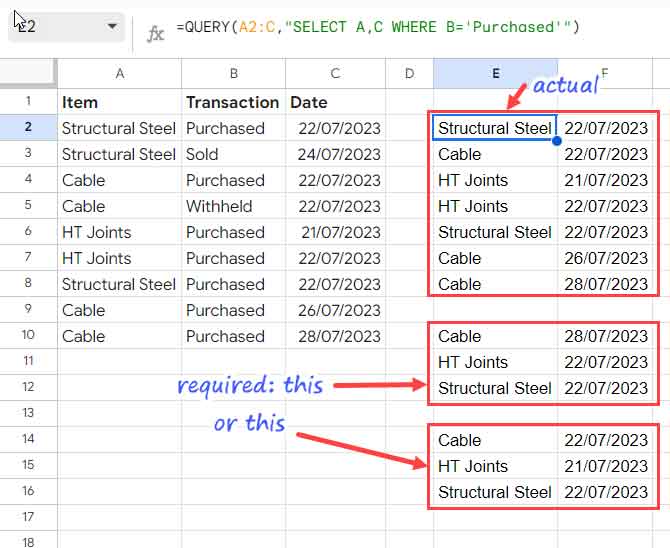
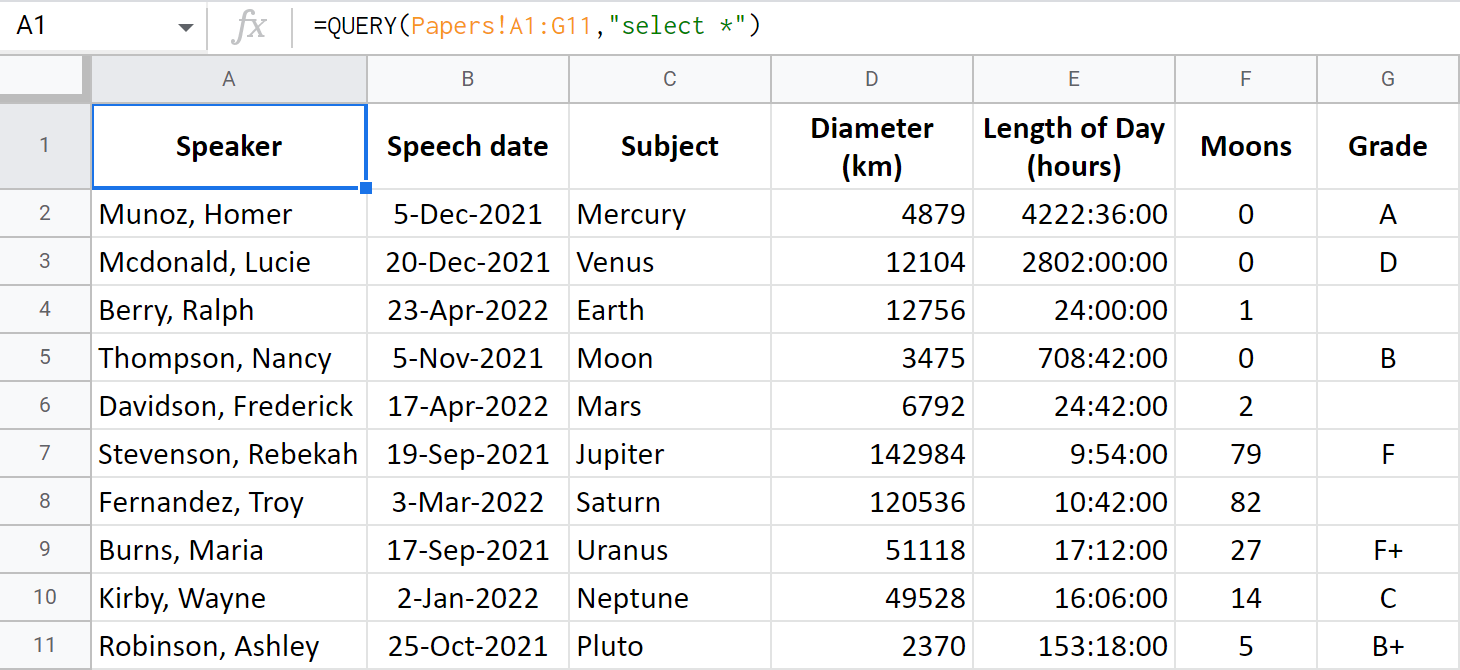
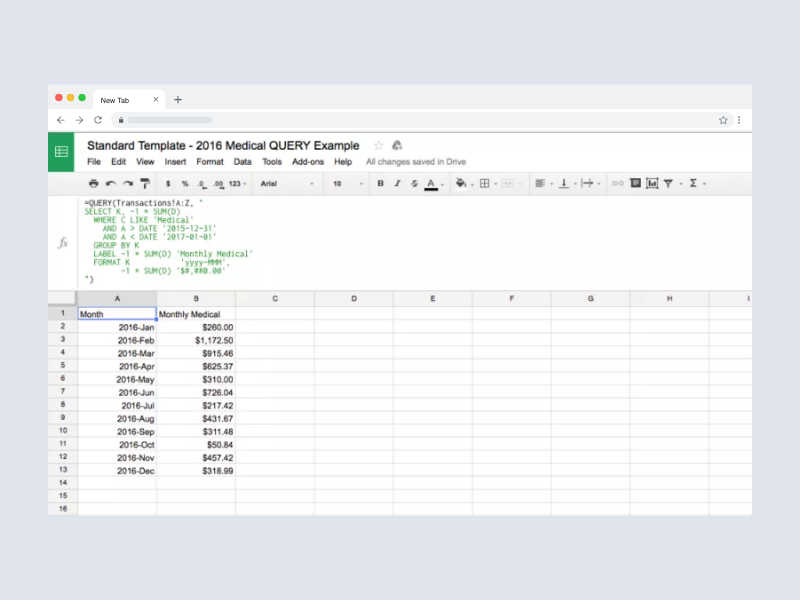
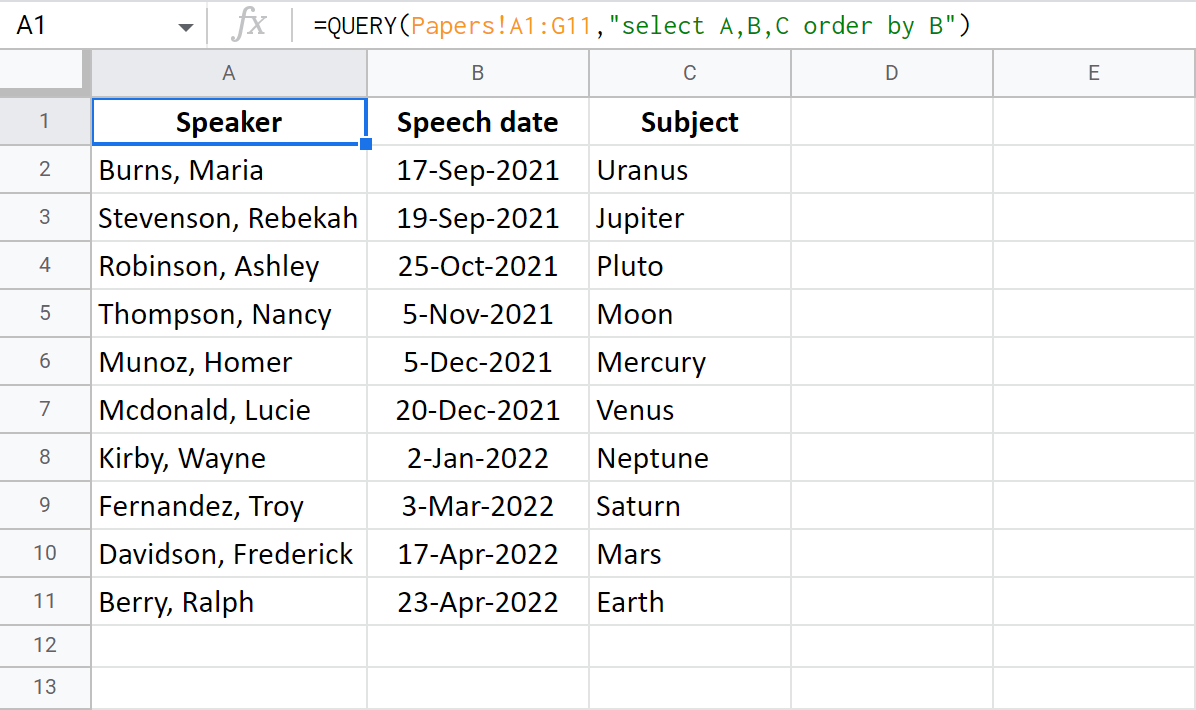
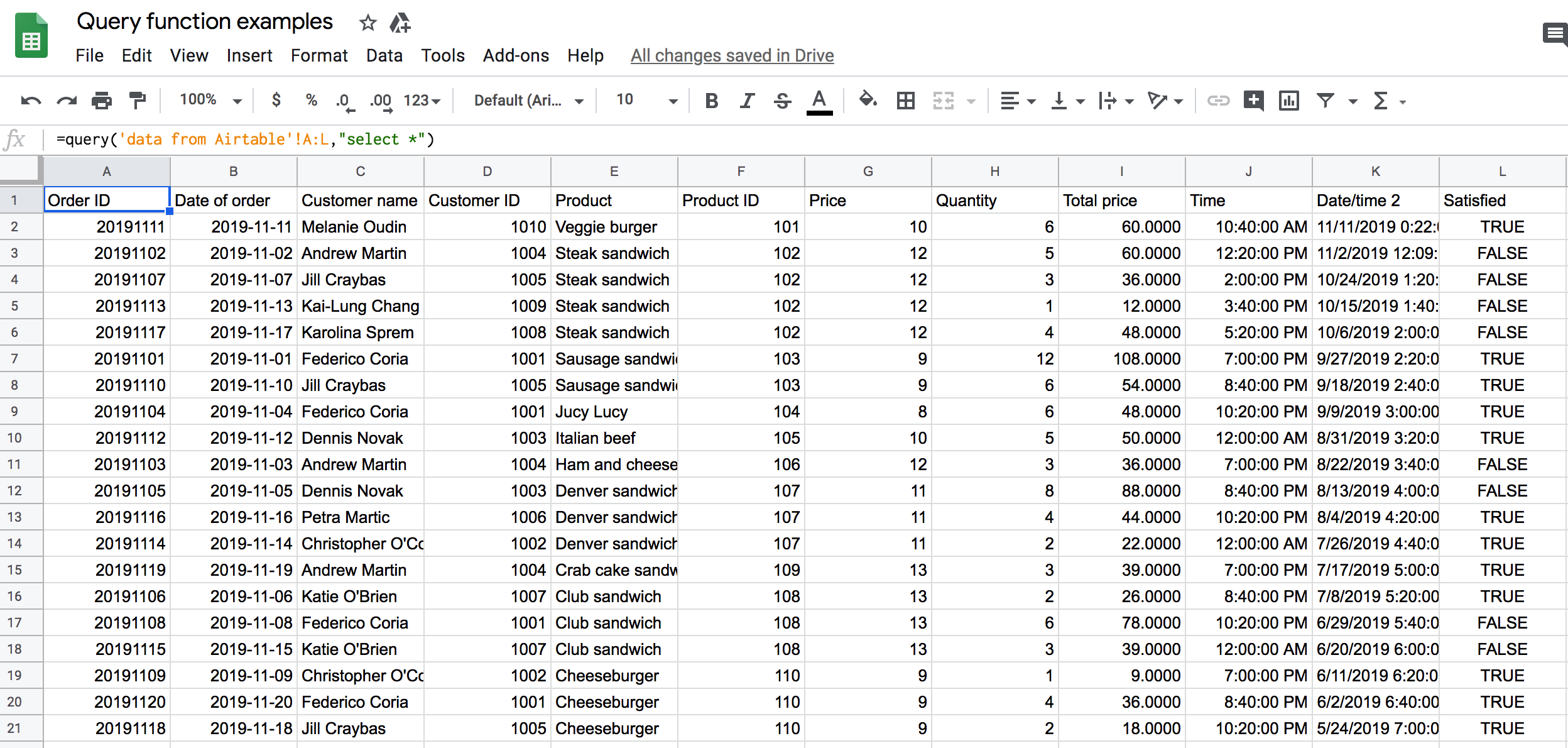
Google Sheets Query Return Headers - Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an.
Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses.
Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label.
How to Return Unique Rows in Google Sheets QUERY
When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query.
Google Sheets Query How to Remove Header from Results
Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. Query can accept either col notation or.
How to use Google Sheets QUERY function standard clauses and an
Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. Modifying the headers is particularly.
How To Insert A Header In Google Sheets SpreadCheaters
It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. Modifying the headers is particularly.
How To Use Google Sheets QUERY Function
It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. Query can accept either col notation or.
Google Sheets QUERY Function Tutorial 2023 Coupler.io Blog
It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the.
How to Use Google Sheet Query in GoogleSheet, How Does It Work? by
When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select.
How to use Google Sheets QUERY function standard clauses and an
When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query.
Google Sheets Query Honest Guide with Formulas and Examples Coupler
Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. Query can accept either col notation or.
Google Sheets QUERY Function Tutorial 2025 Coupler.io Blog
When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. Query can accept either col notation or a, b notation. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an. Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query.
Query Can Accept Either Col Notation Or A, B Notation.
Returns rows that match the specified condition using select and where clauses. When using sum (or any other aggregation function), query automatically creates a header row specifying the aggregation performed, e.g. It is possible to modify the headers returned by the query function using label. Modifying the headers is particularly interesting when an.