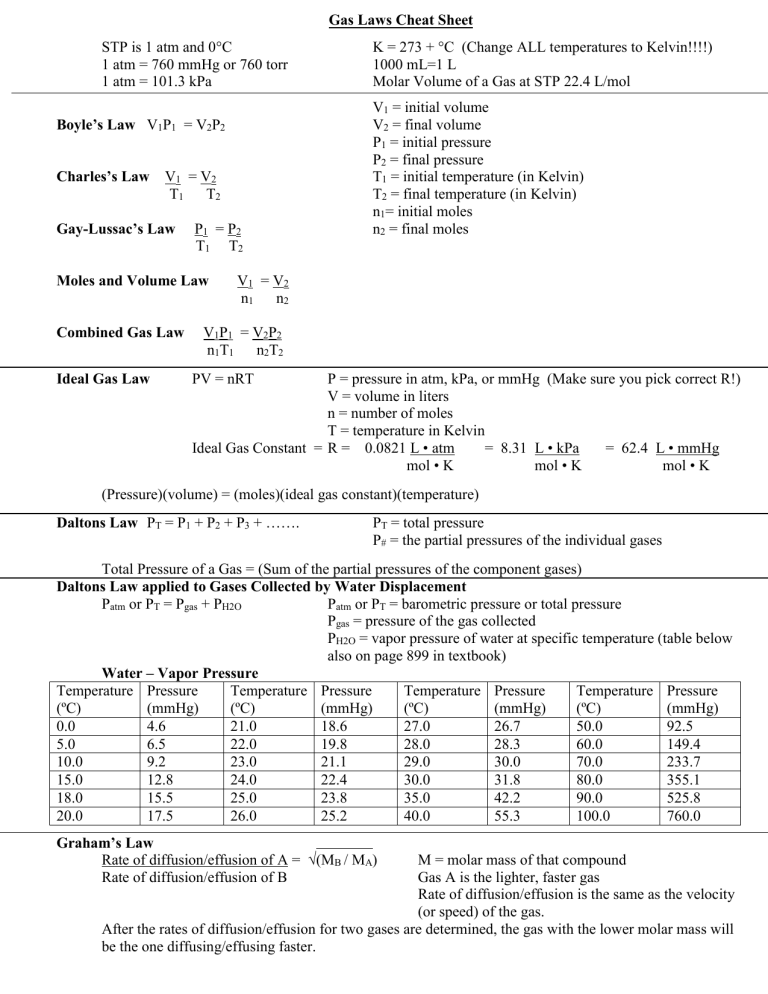
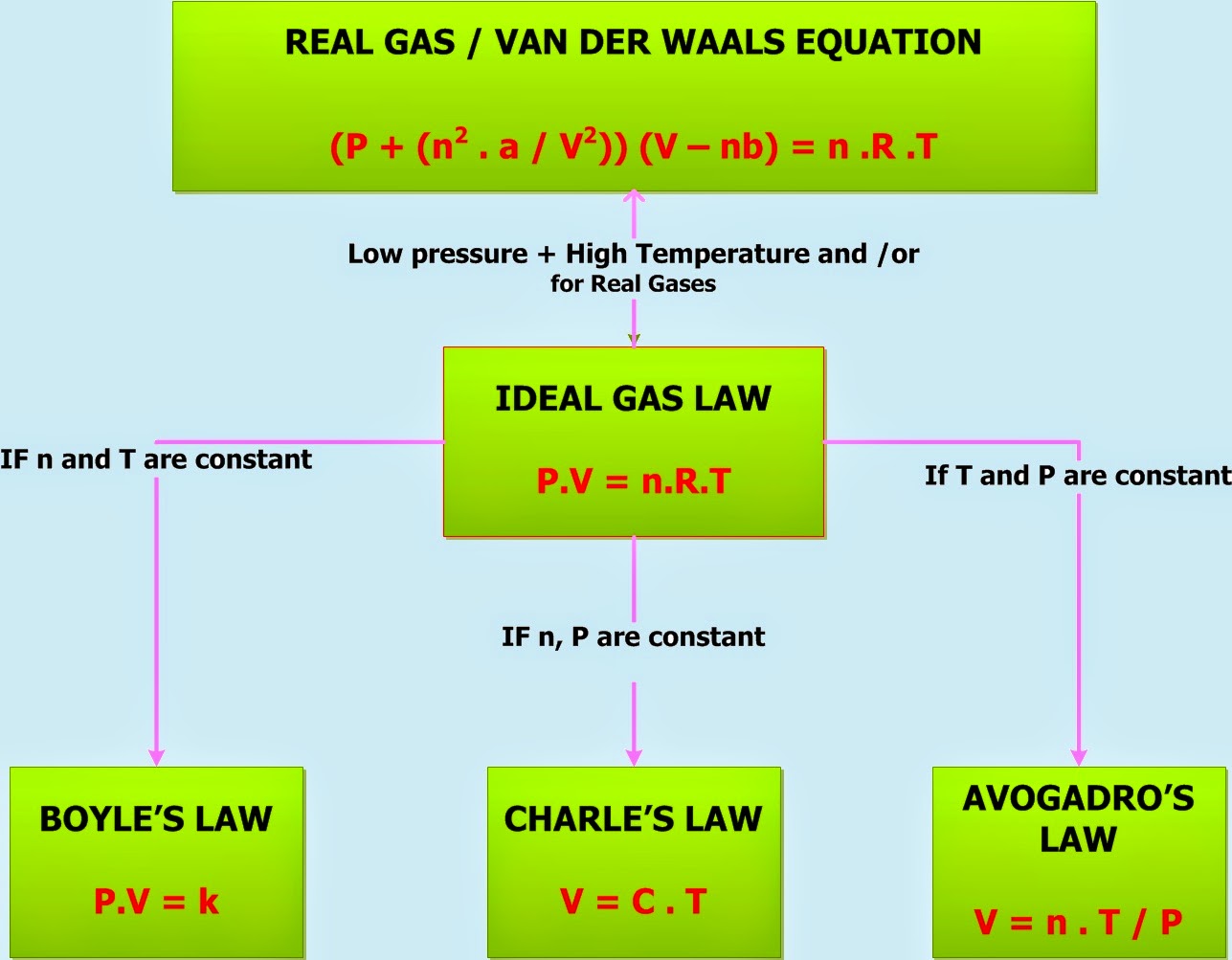
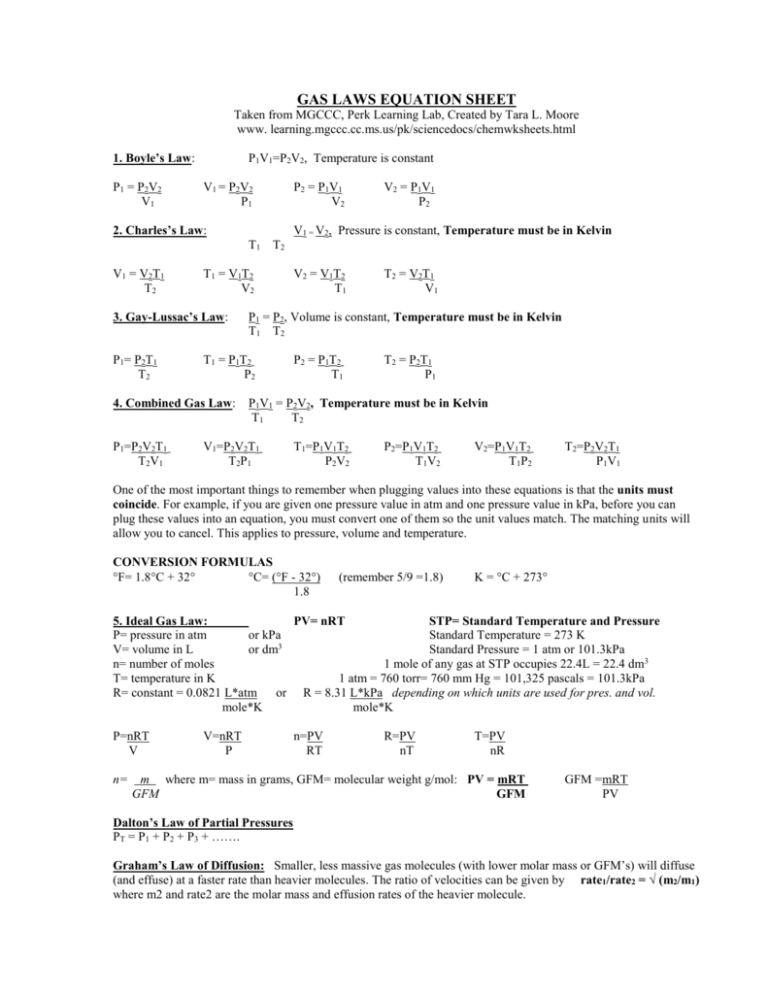
Gas Laws Formula Sheet - The distance between particles is great. Gas particles are neither attracted to. When collecting a gas over a liquid (usually water) you need to subtract how much pressure is coming from the liquid’s vapor in order to. Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement of water. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which have mass.
Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement of water. Gas particles are neither attracted to. When collecting a gas over a liquid (usually water) you need to subtract how much pressure is coming from the liquid’s vapor in order to. Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which have mass. The distance between particles is great. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =.
Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. The distance between particles is great. Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement of water. Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which have mass. Gas particles are neither attracted to. When collecting a gas over a liquid (usually water) you need to subtract how much pressure is coming from the liquid’s vapor in order to.
Ideal Gas Law — Overview & Calculations Expii
Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement of water. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. The distance between particles is great. When collecting a.
Chemistry GAS LAWS All Formulas for engineering& jee/neet 2021
Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which have mass. Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement.
Gas Law Formulas Sheet
Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement of water. Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which.
Gas Law Formulas Sheet
The distance between particles is great. Gas particles are neither attracted to. When collecting a gas over a liquid (usually water) you need to subtract how much pressure is coming from the liquid’s vapor in order to. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of.
Gas Laws Cheat Sheet Formulas & Constants
The distance between particles is great. When collecting a gas over a liquid (usually water) you need to subtract how much pressure is coming from the liquid’s vapor in order to. Gas particles are neither attracted to. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of.
Gas Law Formulas Sheet
When collecting a gas over a liquid (usually water) you need to subtract how much pressure is coming from the liquid’s vapor in order to. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. The distance.
How To Use Combined Gas Law at Joan Ray blog
Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which have mass. The distance between particles is great. Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement of water. Gas particles are neither attracted to. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters.
Gas Laws Equation Sheet Formulas & Conversions
Gas particles are neither attracted to. When collecting a gas over a liquid (usually water) you need to subtract how much pressure is coming from the liquid’s vapor in order to. Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which have mass. The distance between particles is great. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa,.
All Gas Law Formulas
The distance between particles is great. Gas particles are neither attracted to. Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which have mass. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. When collecting a gas.
Gas Law Formulas Sheet
Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement of water. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. When collecting a gas over a liquid (usually water).
When Collecting A Gas Over A Liquid (Usually Water) You Need To Subtract How Much Pressure Is Coming From The Liquid’s Vapor In Order To.
The distance between particles is great. Ideal gas law pv = nrt p = pressure in atm, kpa, or mmhg v = volume in liters n = number of moles t = temperature in kelvin ideal gas constant =. Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles, which have mass. Gas collection over water a mixture of gases results whenever a gas is collected by displacement of water.